Table of Contents

Introduction: Agriculture Sector in India
The agriculture and allied sectors form the backbone of the Indian economy, contributing significantly to the nation’s Gross Value Added (GVA) and providing livelihood to a large portion of the population. This article delves into the key aspects of India’s agriculture sector, including production statistics, export figures, and recent initiatives outlined in the Union Budget 2023. This comprehensive overview will help aspirants of UPSC, State PSCs, and other competitive exams gain valuable insights into the sector.
Contribution to GDP and Employment
- Agriculture is the primary source of livelihood for approximately 55% of India’s population.
- The agriculture sector in India holds the record for having the second-largest agricultural land in the world.
- Gross Value Added: The agriculture and allied sectors accounted for 18.3% of India’s total GVA in FY 2022-23, showing an upward trend.
Major Agricultural Products
India holds significant positions globally in the production of various agricultural commodities:
- Milk: India contributes 24% of global milk production, making it the largest producer in the world.
- Millets: India is the largest producer of millet, with 15.48 million hectares under cultivation.
- Sugar: India is the largest producer of sugar globally.
- Coconuts, Black Tea, Ginger, and Turmeric: Largest producer.
- Cashew Nuts and Tea: 2nd largest producer.
- Fruits and Vegetables: 2nd largest producer.
- Accounts for 10% of the world’s fruit production.
- Leading producer of mangoes, bananas, sapota, and acid lime.
- FDI in agricultural sector: According to the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), the Indian food processing industry accounts for 1.85% of total FDI inflows received.
Agricultural Production Estimates for 2023-24
- Total Food Grains: Estimated at 3288.52 Lakh Tonnes.
- Rice: Estimated at 1367 Lakh Metric Tonnes (LMT).
- Maize: Estimated at 356.73 Lakh Tonnes.
- Moong: Estimated at 14.05 LMT.
- Kharif Pulses: Total production estimated at 71.18 LMT.
- Oilseeds: Total production estimated at 395.93 Lakh Tonnes.
- Soybean: Estimated at 130.54 LMT.
- Groundnut: Estimated at 78.29 LMT.
- Sugarcane: Estimated at a record 4425.22 Lakh Tonnes.
- Cotton: Estimated at 325.22 Lakh Bales (170 kg each).
- Jute & Mesta: Estimated at 92.59 Lakh Bales (180 kg each).
- Total Horticulture Production: Estimated at about 352.23 million tonnes in 2023-24.
Source: Invest India
Export Figures
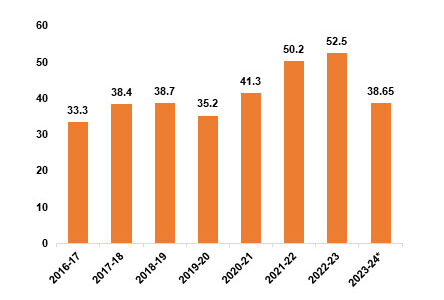
*Note: Until January 24
Source: The Ministry of Commerce & Industry
Overall Agricultural Exports:
- 2022-23: US$ 52.50 billion
- 2021-22: US$ 50.2 billion
- 2020-21: US$ 41.3 billion
April-January 2024:
- Value of Exports: US$ 38.65 billion
Agri & Allied Products:
- 2020-21: US$ 37.3 billion (17% growth over 2020-21)
Rice Exports:
- 2022-23: US$ 11.14 billion
- 2021-22: US$ 9.67 billion (15.22% growth)
Coffee Exports:
- 2023: 1146.2 million tonnes (12.3% growth)
Marine Products:
- 2022-23: US$ 8.07 billion
Key Initiatives by the Government:
- Organizing B2B exhibitions in different countries.
- Exploring new potential markets with product-specific and general marketing campaigns.
- Creating a product matrix for 50 agricultural products with strong export potential.
- Recognizing 220 labs to provide testing services for a wide range of products to support exporters.
Export Destinations:
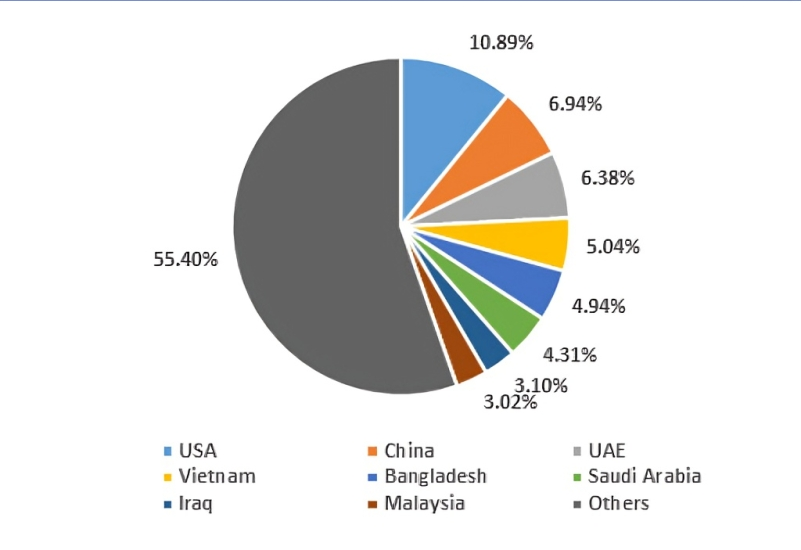
- Key Importers of India’s Agricultural Products (2023-24): As of 2023-24 (until January 2024), the largest importers of India’s agricultural products are:
- USA: The largest importer, with agricultural imports worth US$ 4.20 billion, representing 10.89% of India’s total agricultural exports.
- China
- UAE
- Bangladesh
- Focus on Marine Products: The USA and China are particularly significant as they are the major importers of India’s marine products, which include fish, shrimp, and other seafood.
- Government Initiatives to Boost Agricultural Exports:
- Virtual Buyer-Seller Meets (V-BSM): To promote Indian agricultural and processed food products, especially those registered with geographical indications (GI), the Government of India has organized virtual buyer-seller meets. These events facilitate direct interactions between Indian sellers and international buyers.
- Establishment of Agri-Cells: To further support and enhance agricultural exports, the Indian government has established Agri-Cells within its embassies in key countries. These Agri-Cells are tasked with providing real-time information and assistance to promote Indian agricultural products. The goals of these cells include improving trade relations, encouraging tourism, fostering technological collaboration, and attracting investment. The countries with Indian Agri-Cells include:
- Vietnam
- USA
- Bangladesh
- Nepal
- UAE
- Iran
- Saudi Arabia
- Malaysia
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- China
- Japan
- Argentina
Organic Farming in India
- Organic Farmers: India has the highest number of organic farmers in the world, totaling 44.3 lakh.
- Organic Farming Area: 59.1 lakh hectares under organic farming by 2021-22.
- Organic Products: Includes a wide range of food products such as oil seeds, fiber, sugar cane, cereals, millets, cotton, pulses, aromatic and medicinal plants, tea, coffee, fruits, spices, dry fruits, vegetables, processed foods, and non-edible products like organic cotton fiber.
- Government Support for Organic Farming in India: The Government of India (GOI) has been actively promoting organic farming through various dedicated schemes and initiatives:
- Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY): This scheme encourages traditional organic farming methods to enhance soil health and organic production.
- Mission Organic Value Chain Development in the North East Region: Aimed at developing organic farming in the North East region, this mission focuses on value chain development to benefit farmers. Value chain development is a process to bring a product or service to consumers, including production, research, marketing, and distribution.
- Dedicated Web Portal – Jaivikkheti.in: The government has launched an online platform, www.Jaivikkheti.in, to facilitate the direct sale of organic products from farmers to consumers across the country.
Key Government Initiatives
The Indian government has implemented several initiatives to boost agricultural productivity, ensure farmers’ welfare, and promote sustainable practices. Notable schemes and policies include:
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN): Provides direct income support to farmers.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): Offers crop insurance to protect farmers against crop loss due to natural calamities.
- Soil Health Card Scheme: Aims to promote soil testing and judicious use of fertilizers.
- National Agriculture Market (e-NAM): An online trading platform to create a unified national market for agricultural commodities.
Union Budget 2023 Highlights
- Agricultural Credit Target: INR 20 lakh crore with a focus on animal husbandry, dairy, and fisheries.
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat Horticulture Clean Plant Program: INR 2200 crore to promote high-value horticulture crops.
- Agricultural Accelerator Fund: To promote startups in rural India.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-Kisan): INR 60,000 crore provision.
- Digital Agriculture Mission: INR 450 crore provision for technology promotion in agriculture.
- PM Matsya Sampada Yojana: Sub-scheme with an outlay of INR 6000 crore.
Challenges for Agriculture Sector in India
Despite the progress, the agricultural sector in India faces several challenges. Here are some of the key issues and their solutions, explained in simple terms:
- Climate Change: Changes in weather patterns affect crop yields.
- Solution: Use advanced farming techniques and resilient crop varieties.
- Water Scarcity: Limited water availability for irrigation.
- Solution: Implement efficient irrigation systems and rainwater harvesting.
- Small Farm Sizes: Many farmers own small plots, making it hard to use modern equipment.
- Solution: Encourage cooperative farming and sharing of resources.
- Future Focus:
- Adopt Sustainable Practices: Use eco-friendly farming methods.
- Leverage Technology: Use tools like drones, sensors, and apps to improve farming.
- Ensure Inclusive Growth: Support all farmers, especially smallholders, with training and resources.
Related Topic:

